ESCI A.S2.O1.A4 Mantle Convection
- Due No Due Date
- Points 0
- Submitting a text entry box or a file upload
- Model how convection currents help distribute heat within the mantle
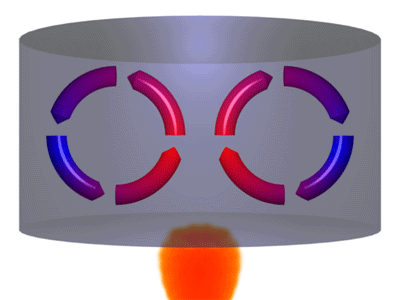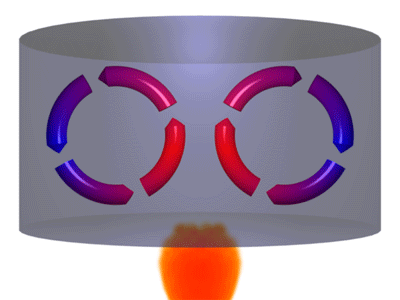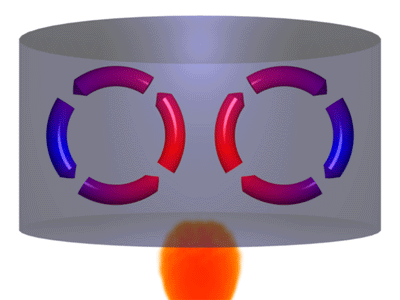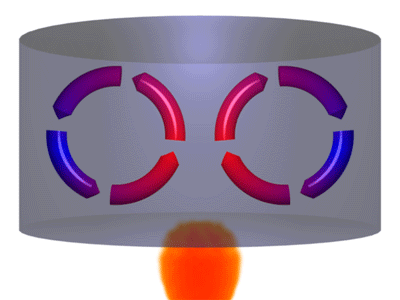
Convection is one of the forces that drive tectonic plate movement. Convection is the movement of a fluid or gas when hotter, less dense material rises up cools off and then sinks back down. The animation above shows a good representation of the convection process.
Of course, observing the convection action underneath Earth's tectonic plates is difficult, to say the least. However, there is a place on Earth's surface that provides a pretty good model for what is occurring. Erta Ale is a volcano in Ethiopia that has been erupting continuously for over 100 years that we know of. It is located in East Africa over one leg of the triple junction that is separating Arabia from Africa. Erta Ale is special, as far as volcanoes are concerned, because it has a lake of molten lava in the center of its caldera.
As magma reaches the surface of this lava lake, it cools to form a dark crust of basalt. However, that crust is constantly in motion as the forces of convection rip it into pieces, move it around, and then drag the cooled stone back into the molten magma below. When shown at normal speeds, this movement is hard to observe, but stop-motion photography can speed up this slow movement to make it easier to observe. Compare the two views below:
Sped Up ESCI A.S2.O1.A4 Lava Lake Tectonics VID Links to an external site.
For a little more information, go check out this site:
http://all-geo.org/highlyallochthonous/2010/05/lava-lake-tectonics/ (Links to an external site.)
Take a close look at the second picture. That banding in the lava is very similar to the magnetic banding that occurs in the basalt sea floor coming from mid-ocean ridges.
Your Assignment: After watching this videos and viewing the website, write a short paragraph explaining the role that convection plays in moving tectonic plates. You may submit it online.
 Find Rubric
Find Rubric